Table of contents
No headings in the article.
build | test | deploy | cleanup
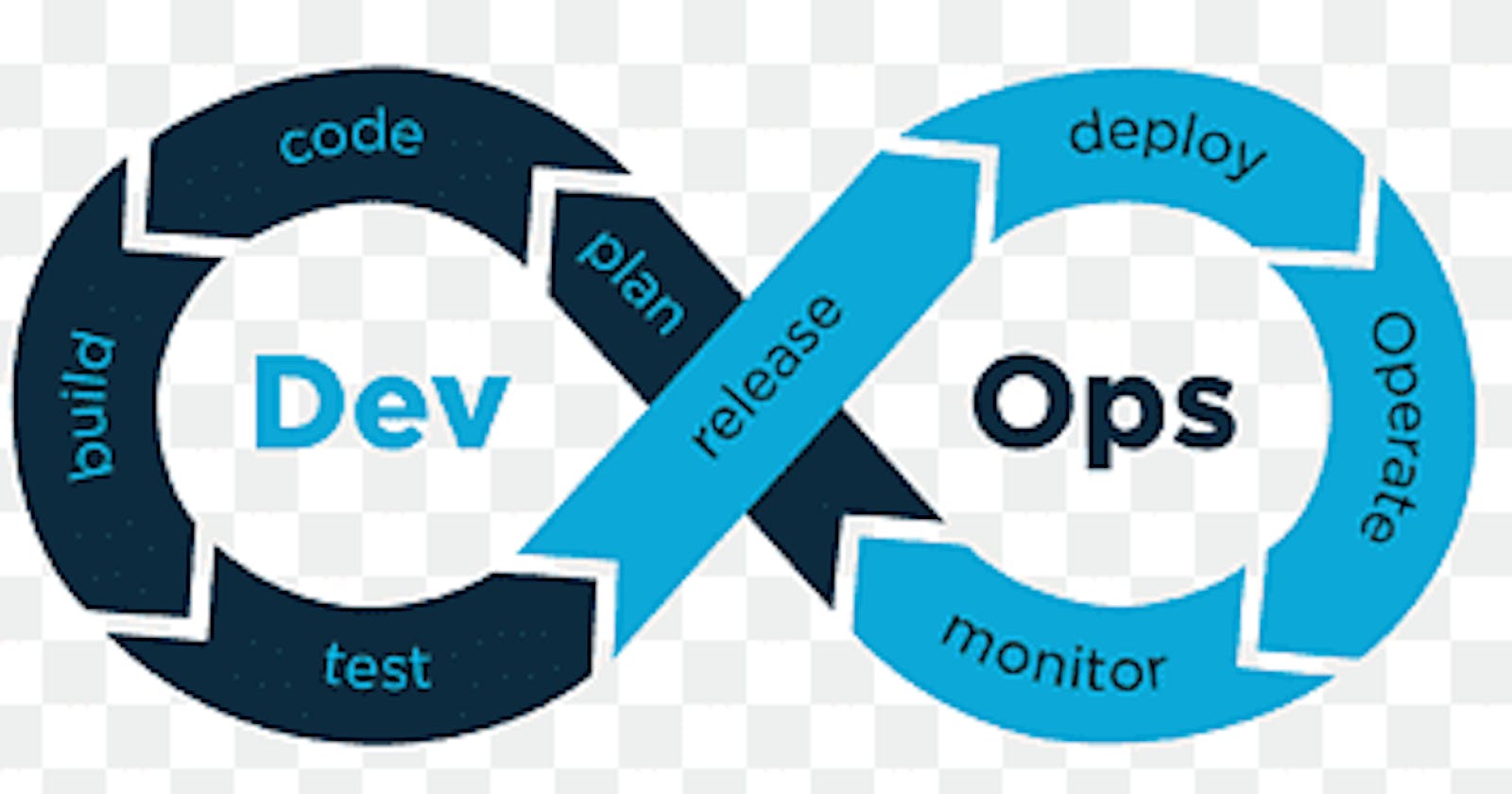
Define the stages of your pipeline: a. Build: Compile the source code and build the application b. Test: Run automated tests to ensure the code meets the requirements c. Deploy: Deploy the application to a staging environment d. Integration: Run integration tests to ensure that the application works with other systems e. Release: Deploy the application to production environment
Create a pipeline definition file: This file will define the pipeline stages and the tasks associated with each stage.
Configure the pipeline: Configure the pipeline to trigger automatically when changes are made to the source code repository. This can be done using a webhook or polling mechanism.
Write a build script: Write a script to compile the source code and build the application. This script can be executed in the build stage of the pipeline.
Write tests: Write automated tests to ensure that the code meets the requirements. These tests can be executed in the test stage of the pipeline.
Configure deployment: Configure the deployment process for your application. This can involve creating a deployment manifest file, configuring a deployment tool, or setting up a continuous delivery system.
Define integration tests: Write integration tests to ensure that the application works with other systems. These tests can be executed in the integration stage of the pipeline.
Release the application: Once the application has passed all the tests, it can be released to the production environment.
Monitor the pipeline: Monitor the pipeline to ensure that it is working correctly and to detect any issues.
Iterate and improve: Continuously iterate and improve the pipeline to make it more efficient and effective